# An In-Depth Guide to Grasping the Various Types of Diamonds
Diamonds have been revered for ages as emblems of opulence, love, and everlasting beauty. Their unparalleled brilliance and strength render them among the most coveted gemstones globally. However, not every diamond is the same. From grading attributes to shapes, origins, and settings, diamonds exist in a multitude of types that suit distinct preferences, financial plans, and uses.
This guide will immerse you in the intriguing realm of diamonds, examining their classifications, grading systems, and favored shapes, as well as ethical considerations and customization possibilities.
—
## **What Distinguishes Diamonds?**
A diamond is a naturally formed gemstone entirely made up of carbon atoms arranged in a cubic crystal lattice. This distinctive atomic configuration provides diamonds their extraordinary hardness—ranking 10 on the Mohs scale—and their capacity to bend light, resulting in the breathtaking sparkle that has enthralled humans for centuries.
Diamonds are treasured not only for their aesthetic appeal but also for their profound symbolism. They are frequently linked to love and dedication, making them a favored option for engagement rings and other sentimental jewelry.
—
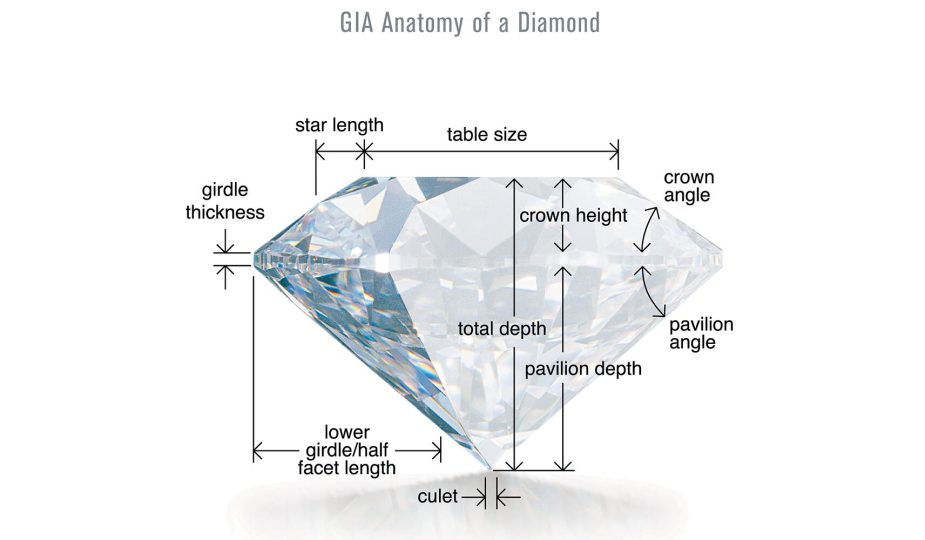
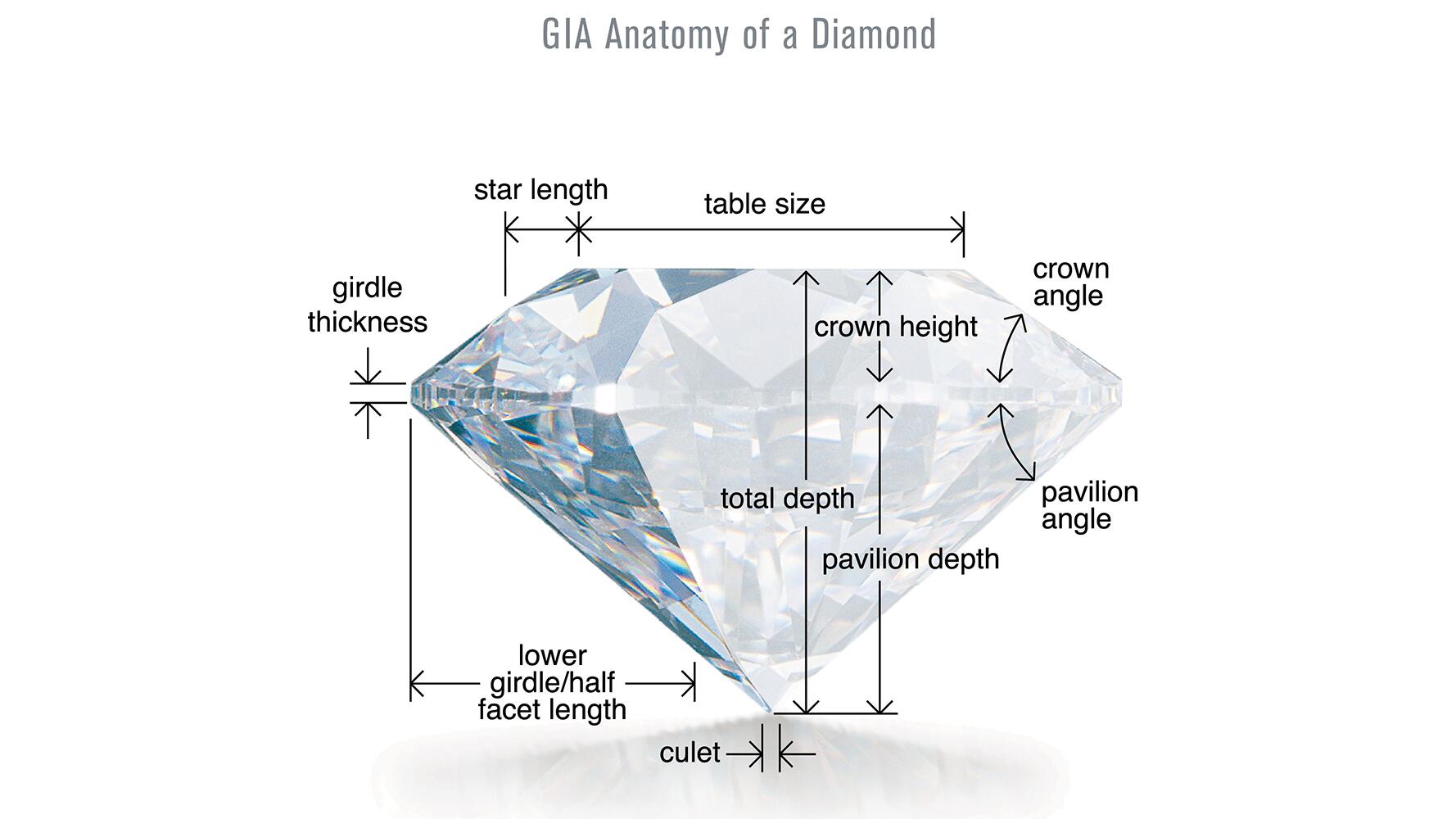
## **Diamond Types: Grading System**
A diamond’s quality is assessed using a standardized grading method based on the “Four Cs”: **Cut, Clarity, Color, and Carat Weight**. These attributes, defined by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), assist in determining a diamond’s worth and attractiveness.
### **1. Cut**
The cut of a diamond pertains to how effectively its facets are shaped and positioned, which has a direct effect on its brilliance, fire, and shimmer. A diamond with an excellent cut reflects light spectacularly, making it seem more vibrant and precious.
– **Grading Scale**: Excellent, Very Good, Good, Fair, Poor.
– **Key Factor**: A large diamond with a poor cut will lack brilliance, whereas a smaller diamond with an exceptional cut can outshine it.
### **2. Clarity**
Clarity assesses the existence of internal faults (inclusions) and surface irregularities (blemishes) in a diamond. A lower number of imperfections leads to a higher clarity grade and increased value.
– **Grading Scale**: Flawless (FL), Internally Flawless (IF), Very Very Slightly Included (VVS1, VVS2), Very Slightly Included (VS1, VS2), Slightly Included (SI1, SI2), Included (I1, I2, I3).
– **Key Insight**: Many inclusions are microscopic and do not detract from the diamond’s appearance to the unaided eye.
### **3. Color**
Diamonds are evaluated on a color scale ranging from **D (colorless)** to **Z (light yellow or brown)**. Colorless diamonds are the most sought after as they permit maximum light reflection, enhancing their sparkle.
– **Fancy Colors**: Diamonds can also be found in uncommon shades like pink, blue, yellow, and even red. These “fancy-colored diamonds” are greatly valued for their distinctiveness.
– **Most Expensive**: Red diamonds are the rarest and can command prices exceeding $1 million per carat.
### **4. Carat**
Carat pertains to a diamond’s weight, with one carat equating to 200 milligrams. Although larger diamonds are scarcer and pricier, size alone does not determine beauty—cut, clarity, and color are just as crucial.
—
## **Common Types of Diamonds**
Diamonds can be classified according to their origin, treatment, and color. Here are the most prevalent types:
### **1. Natural Diamonds**
Created over billions of years deep within the Earth’s crust, natural diamonds are valued for their rarity and unique formation process. They are the most traditional and desirable type of diamond.
### **2. Treated Diamonds**
Treated diamonds undergo processes such as laser drilling or fracture filling to improve their appearance. Although these treatments make diamonds more affordable, they may compromise durability and are generally considered less valuable than untreated diamonds.
### **3. Lab-Grown Diamonds**
Lab-grown diamonds are produced in regulated environments using sophisticated technology. They are chemically and physically identical to natural diamonds but are more affordable and environmentally sustainable.
### **4. Fancy-Colored Diamonds**
These diamonds naturally occur in vivid shades such as pink, blue, yellow, and black. Their rarity and unique colors render them extremely desirable.
– **Black Diamonds**: Their opaque look stems from graphite inclusions, bestowing upon them a striking and enigmatic appeal.
—
## **Favored Diamond Shapes for Engagement Rings**
The shape of a diamond significantly influences the style and character of a piece of jewelry. Here are some of the most favored shapes:
– **Round Brilliant**: Renowned for its maximum sparkle and classic charm.
– **Princess**: A contemporary, square